ENTIRE: An Encyclopedia of Transcription Factors Across the Human Genome
An open-access platform to discover transcription factor binding sites, quantify binding affinities, and compare regulations across the human genome.
Decode Regulation. Drive Discovery.
Platform Modules
Total Visits
Visits Today
Users Online
Visits (Last 7 Days)
ENcyclopedia of Transcription-factor In Regulatory Elements (ENTIRE)
ENTIRE is designed to span the full spectrum of transcription factors (TFs) across the human genome, enabling systematic insights into their regulatory mechanisms. It is constructed based on our newly-developed in vitro FOOtprinting with DeamInasE (ivtFOODIE) technique, which is a variation from previously developed FOODIE. FOODIE stands for FOOtprinting with DeamInasE, and is a technique that delineates transcription factor binding sites genome-wide with near–single-base precision, at single-molecule and single-cell resolution.
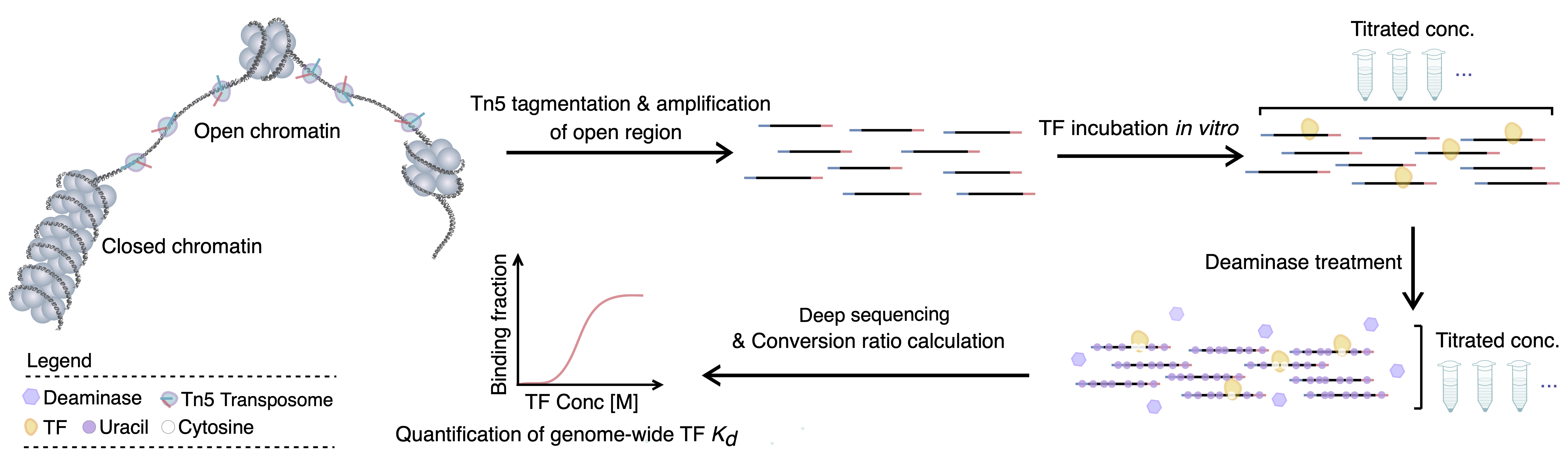
in vitro FOOtprinting with DeamInasE (ivtFOODIE): Genome-wide TF-DNA Affinity Mapping
ivtFOODIE is a high-throughput sequencing-based technique that quantitatively measures equilibrium dissociation constants (Kd) for TFs across the accessible human genome. By using cytosine deaminase footprinting at near–single-base resolution and titrating TF concentrations, ivtFOODIE determines Kd values on thousands of natural genomic binding sites in a simple in vitro setup, offering a powerful foundation for decoding gene-regulatory networks.
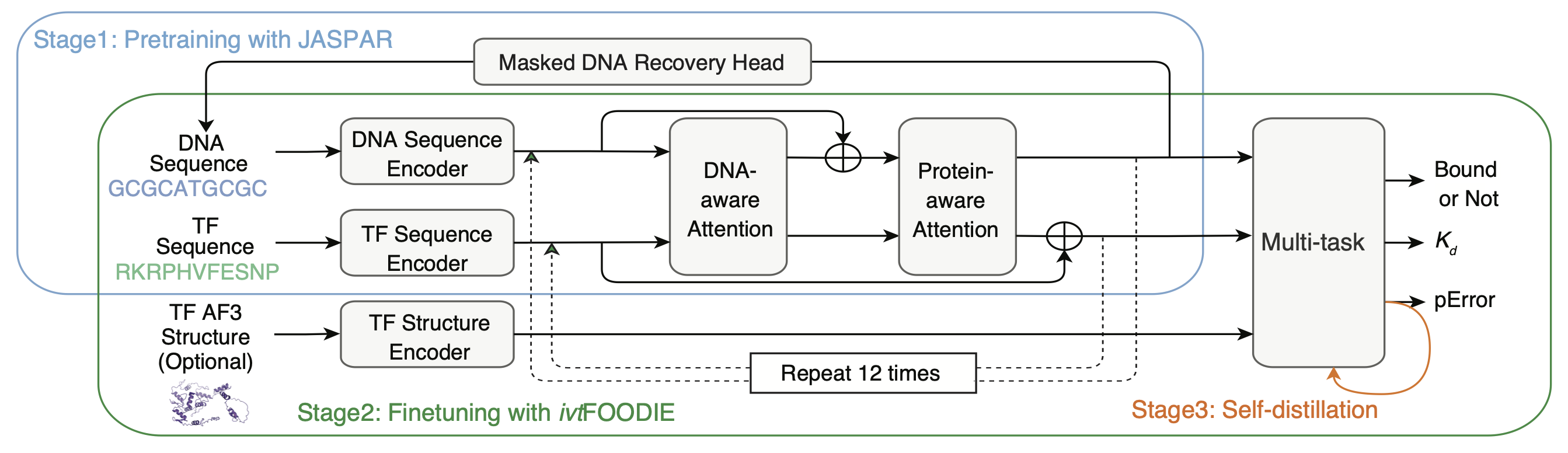
Seq2Kd: From Sequence to Affinity
Seq2Kd is a deep-learning framework that predicts TF-DNA binding affinities for any TF on any DNA sequence. It combines large-scale pre-training on public motif datasets such as JASPAR and HOCOMOCO with fine-tuning on experimentally measured affinities by ivtFOODIE. Seq2Kd generalizes across TF families and quantifies how disease-related SNVs alter TF binding strength, bridging experimental biophysics with genome-wide prediction. Using the Seq2Kd tool, users are able to estimate TF–DNA binding affinity as an equilibrium dissociation constant (Kd) for any given set of DNA and amino acid sequences.
To cite us:
He, R., Dong, W., Wang, Z., Xie, C., Gao, L., Ma, W., Shen, K., Li, D., Pang, Y., Jian, F. and Zhang, J., 2024. Genome-wide single-cell and single-molecule footprinting of transcription factors with deaminase. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 121(52), p.e2423270121.
Seq2Kd Motif: Predicted Motifs of Human Transcription Factors
Seq2Kd Predicted Kd Values with DNA and Amino Acid Sequences
Selected Publications
Contact Us
Questions, collaborations, or feedback? Send us a message and we'll get back to you.
